Affect & Emotion (& Disposition)
What is the most fundamental term discussed in this module and why is it hard to define?
Disposition; it is more subtle because it is a state that can be described as a mood or the energy signature of your body.
What are three qualities of a healthy dispositional state?
Groundedness, awareness, and presence.
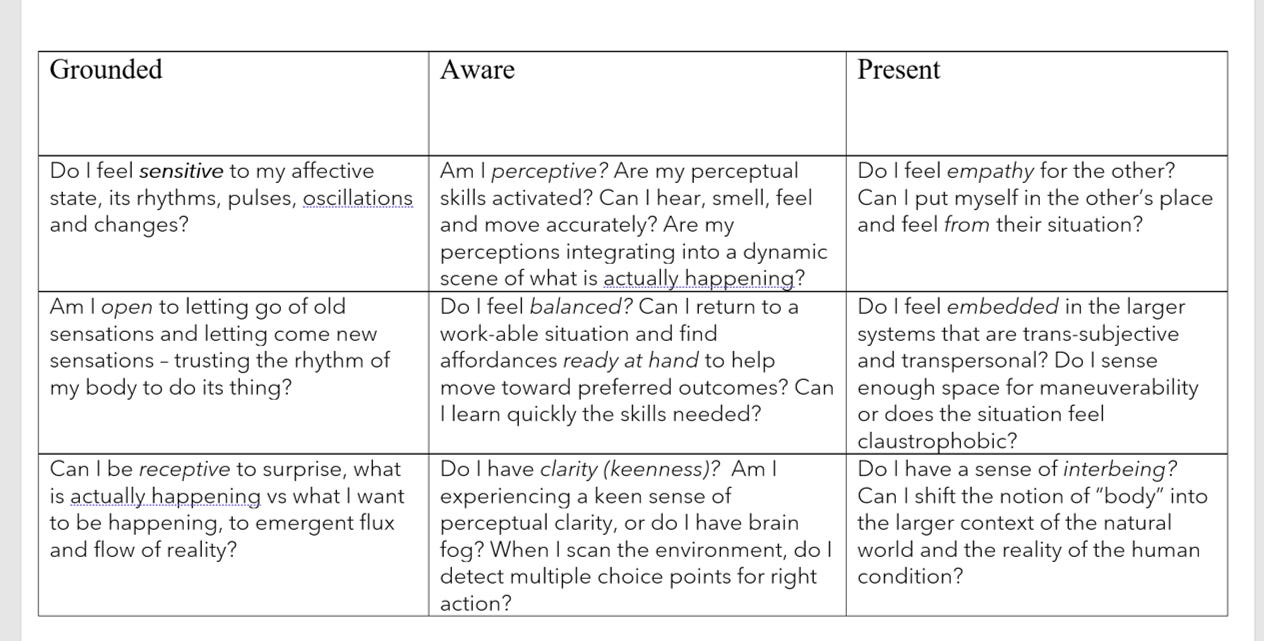
Name two practices that can directly affect your dispositional state.
Breathwork and posture/movement practices like Qigong and Tai Chi.
What are affect streams?
Discrete anatomical, neuro-chemical, and global circulation processes that dispositional states begin to flow through above a particular arousal threshold.
What happens once an arousal threshold is breached?
Affect-laden energy “makes a choice” and action protocols associated with a particular affect stream come into effect.
What does the source define as “affect”?
The particular configuration of the body associated with a particular threshold event that carries forward into discrete anatomical, neuro-chemical, and global circulation processes, triggering specific action protocols.
Name three examples of what “the particular configuration of the body” is referring to in the definition of “affect.”
- Changes in heart rate.
- Whether the pupils dilate or contract.
- Changes in muscle tension.
- Neuro-chemical cocktails flooding into the blood and brain.
- Gut microbiome activity.
- Global responses in the immune system.
- Opponent processing in the brain.
Whose work is the given definition of affect based on?
Jaak Panksepp.
How many discrete affect streams did Jaak Panksepp identify?
Seven.
What is the key difference between the affect itself and its human emotional counterpart?
An embodied affect state does not include all the human-centric, “psychologically conditioned” meaning of what we call human emotion.
What happens to affect in humans above a certain threshold?
It becomes complexified by narrative-memory imaginal overlays and turns into the experience of an emotion.
What can happen when there is too much narrative-imaginal-memory overlay on an affect?
The person can experience “limbic overwhelm” or “emotional flooding.”
How is emotional valence conditioned in early childhood?
By the primary caregivers.
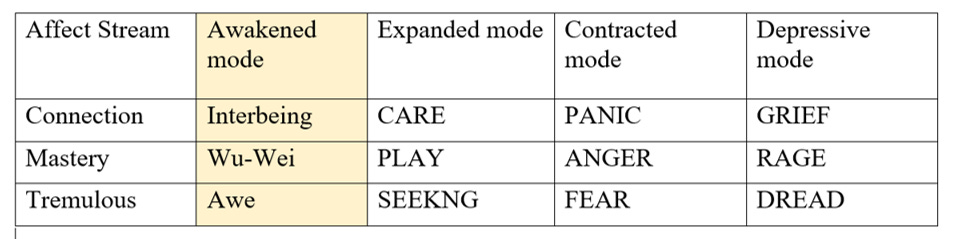
Who organized six of the affects into three primary affect streams for the purposes of healing and clinical work?
Eileen Russel.
What are the three affect streams?
Connection, Tremulous, and Mastery.
How does the source define anxiety?
Anxiety = dispositional state that results in the down-regulation of arousal energy.
What is the difference between guilt and shame?
Guilt is the emotion associated with having done something that one knew was wrong, while shame is a deeper, more complex emotion that occurs when one is put in a double-bind where they must choose between disconfirming an authentic impulse or violating a cultural norm.
How does the sensemaking up-hierarchy operate in an embodied being?
The energy flows from dispositional state to affect streams to narrative-imaginal-mimesis.
What happens to the sensemaking up-hierarchy when the flow of energy is reversed?
It becomes a top-down controlled, conditioned down-hierarchy that is dissociative because what is happening in the present becomes disassociated from the person’s experience.
What intermediate step is missing in a looping sensemaking hierarchy?
Perception.
What is the relationship between action protocols, affect streams, and the sensemaking up-hierarchy?
Robust action protocols, when a specific affect stream is triggered, can move energy in an up-hierarchy from affect-laden drives toward a clarity of perception in the external habitat, keeping it flowing toward actionable choices or real actions that satisfy the arousal state.
When is the information from experience updated in the memory stack?
During sleep, when working current memory processes are downloaded to deeper, episodic memory stacks, completing the descending global updating of the sensemaking up-hierarchy.
This is just a sample set of flashcards. You can use these as a starting point and create more flashcards based on your own understanding of the content. Remember to follow the principles of good prompt writing as described in the source material, such as focusing on one detail at a time, being precise about what you are asking for, and making sure your prompts are tractable and effortful.